Severe aortic stenosis is a when your aortic valve becomes diseased (stenotic). The valve leaflets become stiff and thickened and have a difficult time opening and closing. This makes your heart work harder to pump blood to the rest of your body. A diseased valve affects your health and limits your daily activities.
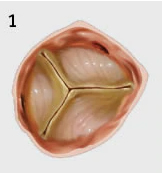
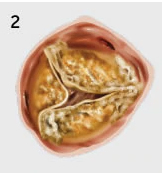
Some causes of severe aortic stenosis include:
Symptoms of severe aortic stenosis include, but may not be limited to:
Certain medications may ease some of the symptoms of severe aortic stenosis.
A tiny balloon is inflated in the aortic valve to try to improve blood flow, but this treatment provides only temporary relief.
Open-heart surgery is done to remove the damaged valve and replace it with an artificial valve. Patients usually need to stay in the hospital for a week or more, before beginning a long period of recovery.
LEARN ABOUT SAVRTAVR is less invasive than open-heart surgery. The doctor will make a small incision, insert a thin, flexible tube into an artery, and guide the heart valve to your heart to replace the function of your diseased valve or failing surgical valve. LEARN ABOUT TAVR
Your heart team will conduct tests to help determine the best treatment plan for you. These tests will tell your doctor:
DISCLAIMER: The content of this document is meant for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment in any manner. Nothing herein should be construed as a promotion or solicitation for an indication for any product which is not authorized by the laws and regulations of your country of residence. Responses to a treatment may vary from patient to patient. Always consult your physician if you have any questions or concerns about your health.